The terms “Spina” and “Bifida” are Latin words that mean spine and split respectively. It is a congenital malformation or a birth defect, which exists due to a combination of environmental and genetic factors. It is a phenomenon where a baby’s spinal cord fails to develop or close properly in the mother’s womb, leaving the backbone and membranes around it to be exposed.
History of spina bifida
Professor Nicolaus Tulp of Amsterdam made the first formative description of the disease around 12,000 years ago. Thereafter, the grouping of symptoms for this disease was brought about in the year 1761. However, effective solutions for this condition were available only in the late 1950s. As a result, the successive years brought about a drastic change in survival rates, with an estimated increase of 80% success in the 1990’s.
Today, in the 21st century, we are fortunate enough to have access and methods for early detection, prevention, and treatment of spina bifida.
Types of spina bifida
Spina Bifida can be mild or severe and is of the following types.
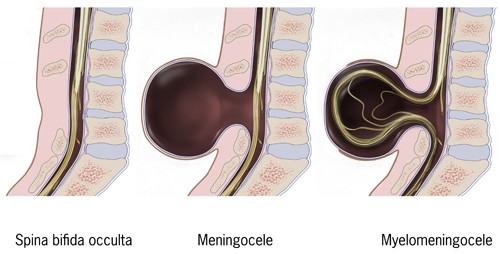
- Spina Bifida Occulta – No or mild signs, hairy patch, dark spot or swelling on the back at the site of the gap in the spine
- Closed neural tube defect– Spinal cord is marked by a malformation of fat, bone, or membranes sometimes causing partial paralysis and bowel problems
- Meningocele – Sac, fluid, or cyst present at the gap in the spine
- Myelomeningocele – Incomplete spinal canal causing the tissues covering the spinal cord or meninges to stick out of the back
Causes of spina bifida
Although there is no specific known cause for spina bifida, the predominant cause remains to be the deficiency of folate in a woman during pregnancy. In fact, lack of folate increases the risk of not just spina bifida but also other neural tube defects in the newborn.
Among other factors known to induce spina bifida in newborns are –
- Genetic or family history of Spina bifida
Couples that have had any one of their children born with the condition face a 20% increase in risk towards having their next child with Spina bifida. - Race and Sex
Spina bifida is more frequent amongst Whites and Hispanics than Asians. Moreover, baby girls are affected more often than boys. - Obesity
Women who have poor nutrition and unhealthy eating habits tend to gain weight before pregnancy. They are, therefore, more at risk of delivering babies with spina bifida than women of average weight. - Diabetes
Elevated blood sugar levels and poor management of diabetes is a known risk factor for spina bifida. - Antiseizure and other medications given during pregnancy
Certain medications like Depakene and Carbamazepine increase the risk of spina bifida as they block the body’s ability to process and store folic acid. - Hyperthermia
Increased body temperature during the early weeks of pregnancy increases the risk of spina bifida.
Prevention of Spina bifida
Spina bifida can be prevented by early diagnosis of a probable folate deficiency. Pregnant women are highly recommended to increase their intake of folate either by consuming natural foods rich in folate, such as breads and beans, egg yolks, citrus fruits and juices, dark green vegetables, such as broccoli and spinach, rice and cereals, or take the appropriate folic acid supplements as prescribed by their doctors. WHO’s recommended dose is around 400 micrograms of folic acid per day.
Great sources of Folate
Treatment of Spina Bifida
In order to enable children, afflicted with the disease, to achieve a certain degree of functional comfort and independence, various treatments have been effectuated over the years.
Children born with Spina bifida Occulta or closed neural tube defect need no immediate treatment, but may in certain cases require monitoring for signs and symptoms of spinal cord dysfunction if it occurs. In case of Meningocele, the infant requires surgery for the removal of the cyst or sac.
If the infant has been diagnosed with spina bifida during the mother’s pregnancy, a prenatal surgery has to be performed. The first type of prenatal surgery is the Open Fetal surgery where the uterus is opened and spina bifida repair is performed. The second prenatal surgery type is Fetoscopy, where an incision of 3-4mm is made in the abdomen and an endoscope is inserted via the abdominal wall and the uterus.Sometimes, doctors also recommend the mother to deliver her child by a cesarean section (C-section) instead of a natural vaginal delivery.
In severe cases like in Myelomeningocele, a postnatal surgery is performed to place the spinal cord and nerves back in place. In cases where even after subsequent attempts the deformity persists in the child, physical therapy and continuous treatment is mandated for the baby.















